Wheaton Branch Dam Overtopping Project
The Wheaton Branch Regional Stormwater Management Pond was originally designed and constructed in 1979 for flood control to protect downstream properties in the Woodman Avenue and Inwood Avenue areas as well as further downstream along Wheaton Branch and Sligo Creek. The pond receives runoff from a 770-acre watershed that is comprised of just over 50% impervious land cover, including a large shopping mall and commercial complex around the Wheaton Metro Station, and other commercial and residential developments between Wheaton and Dennis Avenue along the intensively developed Georgia Avenue corridor. The pond was retrofitted to its current configuration as a three celled wet pond in 1988 to add water quality treatment in addition to flood control. Overall, the pond provides many benefits downstream in lower Wheaton Branch and Sligo Creek including; 1) reduced stream channel erosion as stormwater captured in the pond is slowly released after storms, 2) water quality treatment as sediment and pollutants settle out in the pond, and 3) flood control.
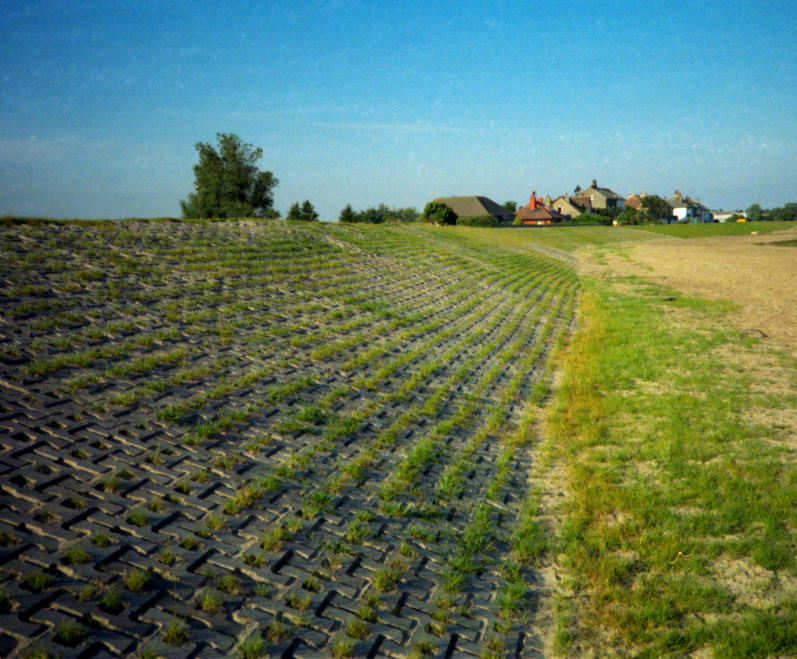
As Part of the 1988 retrofit, an approximately 500-foot spillway was added on top of the dam to help pass the Probable Maximum Flood (PMF). The PMF is a theoretical flooding event resulting from the greatest depth of precipitation for a given duration that is physically possible over a particular geographic location at a given time of year. The spillway was protected by adding grouted gabions at the top of the dam and Enkamat on the downslope side. Information obtained from a 2018 analysis found that the dam embankment is not adequately protected during a PMF event.
Project Details
| Project Status | In Design |
| Construction Timeline | Winter 2024 - Spring 2025 |
| Project Cost: | TBD |
| Watershed: | Anacostia River |
| Contact: | DEP Engineer: Leying Zhang Leying.Zhang@MontgomeryCountyMD.gov 240-777-7727 |
| Contact: | Doug Marshall Douglas.Marshall@montgomerycountymd.gov (240) 777-7767 |
| Fact Sheet: | Wheaton Branch Dam Overtopping Protection Project Fact Sheet (PDF) |
| Public Hearing Public Meeting: |
April 11, 2024, 7-8pm (via Zoom) October 12, 2021, 7-8 pm (via Zoom) |
| *Information is subject to change | |
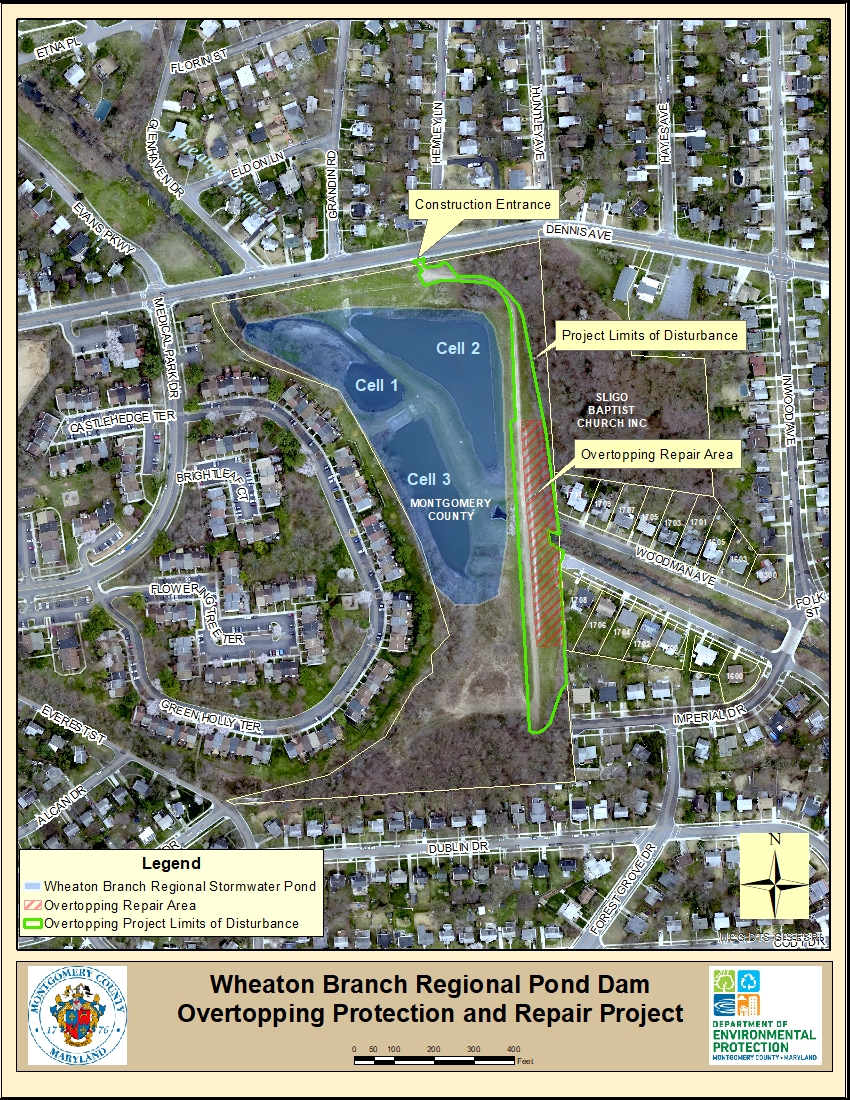
Project Design Plan
The County identified three alternatives to reinforce the Wheaton Branch dam embankment to withstand the erosive force of water flow during a PMF storm event, including: gabion baskets, an articulated concrete block (ACB) system and artificial turf (Hydroturf). After a thorough review of the overtopping protection alternatives, the ACB system was selected because of it's strength and durability. ACBs are a matrix of precast concrete blocks that are cabled together and installed to provide a hard, erosion resistant surface while allowing vegetation to establish within the system. ACB's have historically been used to reinforce slopes that experience higher flows where traditional protection such as riprap do not offer adequate protection.
Each of the Articulated Concrete Blocks is 16"L X 16"W X 5"H and are bound together with polyester cables designed to meet stress requirements. Large rectangular ACB mattresses will be placed on a prepared base consisting of geotextile fabric and a 6 inch bed of gravel to provide safe drainage through the ACB's and down the embankment slope.

Installation of Articulated Concrete Mattress
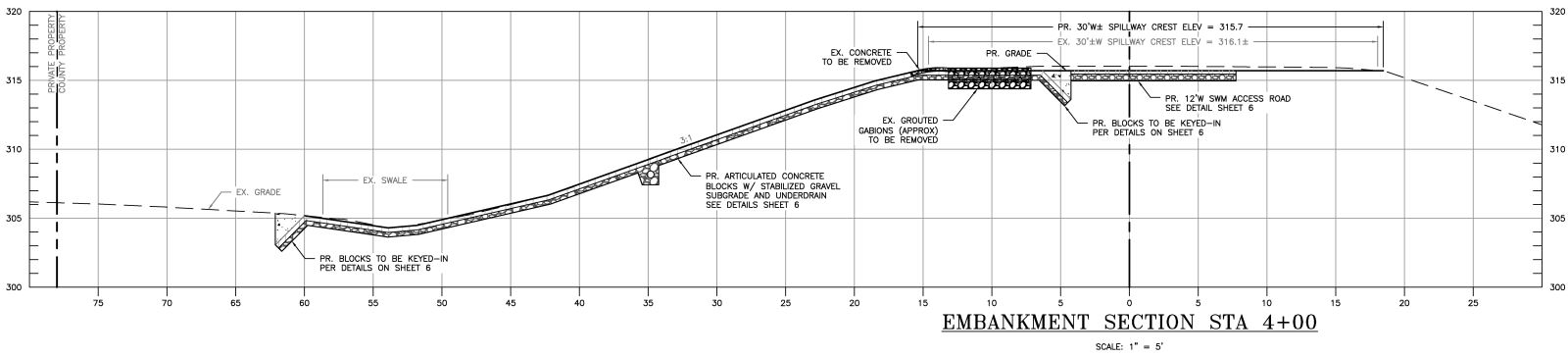
Wheaton Branch Overtopping Project Cross-Section Detail
The ACB mattresses will be keyed into existing soil at the top of the embankment and the bottom as shown in the cross sectional detail above. The ACB system will have approximately 20 percent open void space that will be filled with topsoil and seeded with a meadow seed mix to provide a vegetative cover.
